This is a test.
Relevance: Get a list of properties for a type
properties of type "operating system"
Output:
name of <operating system>: string
release of <operating system>: string
version of <operating system>: version
build of <operating system>: string
architecture of <operating system>: string
machine of <operating system>: string
windows of <operating system>: boolean
unix of <operating system>: boolean
mac of <operating system>: boolean
embedded of <operating system>: boolean
major version of <operating system>: integer
minor version of <operating system>: integer
build number of <operating system>: integer
build number high of <operating system>: integer
build number low of <operating system>: integer
platform id of <operating system>: integer
csd version of <operating system>: string
service pack major version of <operating system>: integer
service pack minor version of <operating system>: integer
suite mask of <operating system>: operating system suite mask
product type of <operating system>: operating system product type
product info numeric of <operating system>: integer
product info string of <operating system>: string
performance counter frequency of <operating system>: hertz
performance counter of <operating system>: integer
ia64 of <operating system>: boolean
x64 of <operating system>: boolean
metric <integer> of <operating system>: integer
boot time of <operating system>: time
uptime of <operating system>: time interval
Relevance: Using information for a type
x64 of operating system
Output:
True
This is because x64 is within the evaluated information of the type "operating system", specifically "architecture".
As seen here:
architecture of operating system
Output:
x86_64
Evaluation time: 0.040 ms
Slightly more complicated example:
build number low of operating system < 9300 and architecture of operating system contains "x86" or architecture of operating system contains "64"
Mixed with light amount of action script:
if{build number low of operating system < 9300}
wait cmd.exe /c mkdir "C:\Users\ewoelfel\Desktop\Tivoli"
endif
Log File Locations
* Windows: C:\Program Files\BigFix Enterprise\BES Client\__BESData\__Global\Logs
* Unix/Linux: /var/opt/BESClient/__BESData/__Global/Logs
* /Library/Application Support/Bigfix/BES Agent/__BESData/__Global/Logs
Start with what people are paying for the company, by finding the market cap of the stock. Ex: GOOG = $289B Now that you know what people are paying for it, what is it actually worth? Simplified value of company = present assets - present liabilities + future earnings, discounted to present values Using these two values (market cap=$ people are paying, and company value=$ it is worth) we can now re-frame your original question. Overvalued companies are those where market cap>company value (people paying more for it than it's worth) and undervalued companies have the opposite relationship, company value>market cap.
Having established that, let's examine how to calculate company value. To reiterate, company value = present assets - present liabilities + future earnings. So there's a present component, and a future component. Let's look at the present component first.
You can find the company's assets and liabilities on its balance sheet, for GOOG, present assets = total assets - goodwill - intangible assets = $78B. Goodwill and intangible assets are removed because they're often imprecise due to being semi-imaginary. Again for GOOG, present liabilities = total liabilities = $21B. So GOOG has tangible assets less total liabilities of $78B-$21B=$57B. Let's go ahead and subtract that from the total market cap, $289B, to get $232B - the future value of GOOG required to justify its value. Future values are uncertain, and therefore are purely estimates. A number of other posts here have given good methods for exploring future revenues/cash flows, so I'll continue to give the big picture. What is GOOG earning? $16.6B cash from operations. Where is that money going? $3.2B to capital investments + $0.3B in share buybacks, and the rest is retained within the company. So $16.6B-$3.2B-$0.3B = $13.1B earned per year at current returns.
Now let's divide the $232B "future value" of GOOG (market cap - present value), by $13.1B to find out how many years it'd take to earn that future value back: 17.7 years. Alternatively, you can divide it the other way to see that each year at $13.3B you're earning 5.6% of the future value. That's pretty decent, but is it fair? Well, it largely depends on what your opinions of GOOG's future prospects are. If you think its growth over the next 17 years will outpace inflation, then you'd likely earn a nice return on it. On the other hand, if you fear too many people taking the Bing challenge and being driven off of cliffs by driverless cars then it would be a bad investment. What we can definitely say is that 5.6% is a reasonable starting point. Not cheap, but also not insanely low.
I'll go ahead and close this with a few notes of caution - most of the companies you'll find that look very very cheap based on these quantitative criteria have very negative qualitative criteria associated with them. This method is best applied to companies you already like, but are unsure whether the price is right.
I brined them overnight in a gallon of water, 10 ounces salt, and 1/2 cup honey. The dry rub is Meathead's Memphis Dust. They were in the smoker at 235 for about 6 hours, with 2 doses of hickory smoke (about 12oz of chips total). 5 hours in, I brushed on the glaze: Mix ¼ cup Ketchup, 3 Tbsp Honey, 2 ½ Tbsp Balsamic Vinegar, 2 tsp Onion Powder, 1 tsp Chili Powder, 4 cloves fresh garlic, 1/2 tsp Garlic Powder, ¼ cup Olive Oil, and 8 dried chilis in a blender. When it's all incorporated, stir in some liquid smoke and bourbon to taste. For the last 15 minutes, I cranked the heat to 400 to caramelize the glaze a little. Remove, rest under foil for 10 minutes or so, and enjoy! What it looked like on the inside. The smoke ring was more prominent than the photo shows.
oh, I also coated them with a little olive oil before shaking on the rub. It helps with adhesion, and it blooms the spices in the rub (a lot of the flavor compounds are fat soluble).
tips: 1) It's just a cheapo vertical smoker. Temp control can be an issue; adding mass helps with stability. bricks, a pizza stone, and unglazed ceramic tile all act as thermal capacitors to hold and evenly distribute the heat. I always use a put a pan of water in with the meat, too. Water does a phenominal job of stabilizing temparure, and steam helps carry smoke into the meat better. 2) These are back ribs, but I've used St. Louis with good results, too. I'm not hardcore in favor of one cut over another, I just use whichever looks the best at the butcher. 3) I don't flip them. Since my smoker is vertical, the bottom rack is hotter than the top, so I do rotate them every couple of hours. I don't mop; if I'm saucing them at all, I'll brush it on about an hour before they come out. Other times, I'll serve the sauce on the side. One thing I will say - don't go overboard with the rub or the sauce. You can always add more on the plate, but you can't take it off. There's delicious pork on those bones; your goal should be to amplify that, not drown it out.
for the chili: I used a mix of Ancho and Guajillo. Arbol also work, and I'll even toss a ghost pepper in sometimes if I'm feeling saucy.
Memphis Dust Recipe Yield. Makes about 3 cups. I typically use about 1 tablespoon per side of a slab of St. Louis cut ribs, and a bit less for baby backs. Store the extra in a zipper bag or a glass jar with a tight lid. Preparation time. 10 minutes to find everything and 5 minutes to dump them together.
Ingredients 3/4 cup firmly packed dark brown sugar 3/4 cup white sugar 1/2 cup paprika 1/4 cup Morton's kosher salt 1/4 cup garlic powder 2 tablespoons ground black pepper 2 tablespoons ground ginger powder 2 tablespoons onion powder 2 teaspoons rosemary powder
About the sugar and salt. I encourage readers to experiment with recipes, and "no rules in the bedroom or dining room" is my motto, but I have gotten some emails that require a response. I appreciate that many of you feel the need to reduce sugar and salt in your diets (although recent research has warned that low salt diets can be just as dangerous as high salt diets), but they are in the recipe for more than flavor enhancement, they help form the crust (a.k.a. called "the bark" by the pros), an important part of the texture of the surface of ribs and slow smoke roasted pork. The salt pulls some moisture to the surface to form a "pellicle" and the sugar mixes with the moisture, caramelizes, and also contributes to the crust. Salt also penetrates the meat far deeper than the spices and there it helps bind moisture. I strongly recommend you leave them in.
There are only about 2 tablespoons of rub on a large slab. Of that about 1 tablespoon is sugar, and 1/2 teaspoon of salt. Some of it falls and drips off during cooking. If you eat half a slab, you're not eating about 1 teaspoon of sugar and less than 1/4 teaspoon of salt. And for those of you who object to white sugar for non-dietary reasons, and use brown sugar instead, you need to know brown sugar is just white sugar with molasses added. It is not unrefined sugar. I use brown sugar for the flavor and white sugar because it improves the bark. You can substitute table salt, but beware that if you do, you should use about 2/3 as much. Read my article on salt.
If you want to cut back on carbs, leave off the sweet barbecue sauce. It has a lot more sugar. Switch to a Lexington sauce which is mostly vinegar, or just eat the pork with rub and no sauce. It's mighty good that way...
About the rosemary. One reader hates rosemary and leaves it out. Trust me, it hides in the background and you will never know it is there. But it is. It is subtle and important in this blend. Substitute thyme or oregano if you must, but I think rosemary is the best choice. If you can find ground rosemary, good for you. It's hard to find. So just grind the rosemary leaves in a mortar and pestle or in a coffee grinder. It will take 2 to 3 tablespoons of leaves to make 2 teaspoons of powder.
About the paprika. If you read my discussion of paprika by clicking the link you'll learn about the different kinds of paprika. In short, garden variety grocery store paprika has little flavor and is used mostly for color. But fresh Hungarian or Spanish paprika have mild but distinctive flavors. If you can find them, they improve this recipe. If you wish, you can use smoked paprika, especially good if you are cooking indoors, or even mix in some stronger stuff like ancho (slightly spicy), chipotle powder, cayenne, or chili powder (not very hot). Chipotle can be quite hot, so be thoughtful of who will be eating your food. I usually go easy on the heat in deference to the kids and wimps (like me) and add it to the sauce or put chipotle powder on the table for the chile heads.
About the ginger. I think it is a very important ingredient. If you don't have any, get some.
Method 1) Mix the ingredients thoroughly in a bowl. If the sugar is lumpy, crumble the lumps by hand or on the side of the bowl with a fork. If you store the rub in a tight jar, you can keep it for months. If it clumps just chop it up, or if you wish, spread it on a baking sheet and put it in a 250°F oven for 15 minutes to drive off moisture. No hotter or the sugar can burn.
2) For most meats, sprinkle just enough on to color it. Not too thick, about 2 tablespoons per side of a large slab of St. Louis Cut ribs. For Memphis style ribs without a sauce, apply the rub thick enough to make a crunchy crust, about 3 tablespoons per side (remember to Skin 'n' Trim the back side). To prevent contaminating your rub with uncooked meat juices, spoon out the proper amount before you start and seal the bottle for future use. Keep your powder dry. To prevent cross-contamination, one hand sprinkles on the rub and the other hand does the rubbing. Don't put the hand that is rubbing into the powder.
3) Massage the rub into the meat at least an hour before cooking. Two to three hours is better.
I was reading articles on Reddit and found this blog post about how to become a lifelong learner. Or, in other words, changing the way you think to realize that there is always potential for growth in your intelligence despite age and time constraints.
Why Become a Lifelong Learner?
You'll earn more
Fifty or sixty years ago, you could finish college and you'd have all the education you needed for the rest of your career. You don't have that luxury in today's job market. Skills that were cutting edge five years ago are likely out of date, and the jobs that we will perform in the next decade or two probably don't even exist yet. If you want to stay competitive in today's job market and potentially earn more money, you need to become an autodidact.
Not only can becoming a lifelong learner help you earn more money in traditional employment, autodidacticism can be the gateway to self-employment and starting your own business. There are countless examples from history of famous folks who learned how to create thriving businesses without any formal education: Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Edison, and Henry Ford to name just a few. Countless not-so-famous business owners became successful without ever earning a sheepskin too, simply by teaching themselves what they needed to know and relentlessly tinkering.
You'll be more interesting and charismatic
Those who met Theodore Roosevelt were always greatly impressed with his ability to hold a conversation with anyone regarding any subject imaginable. Scientists were blown away with Roosevelt's knowledge of complex theories, socialites were smitten with his witty insights about the latest piece by Oscar Wilde, and cowboys out West respected the "Eastern Dude's" understanding of desert wildlife. How did Theodore Roosevelt become such a charismatic, conversational dynamo? By developing the ability to speed read and then devouring books like a hungry lion feasting on a fresh kill. While in the White House, he would read a book every day before breakfast. If he didn't have any official business in the evening, he would read two or three more books, plus any magazines and newspapers that caught his fancy. By his own estimates, TR read tens of thousands of books during his lifetime, including hundreds in foreign languages. As a result, he could connect with anyone, from any walk of life, on something that truly interested the other person.
You'll be a better leader
Being able to connect with others doesn't just make you more interesting. It also makes you much more influential. The greater your knowledge base, the more you can meet people where they are, and the greater the stockpile of solutions you have at your disposal to tackle problems and overcome challenges.
You'll be independent and handy
One thing I admired about my grandpa growing up was all the cool stuff that he knew. He was always tinkering, and it seemed like he knew everything about everything. How to hunt, how to shoe a horse, how to garden (he grew grapes), how to make awesome pancakes. Even after he retired, my grandpa was always learning new things and acquiring new skill sets. For example, he learned how to restore antique horse carriages and old phonograph players. He got so good at it, in fact, that he started restoring antique phonograph players as a small side-business.
Because of my grandpa's diverse range of skills, when something broke or he needed something done, he could do it himself. He didn't have to call and pay an expert to do it for him. If he didn't know how to do it, he went to the library, got some books on the subject, and figured it out.
Lifelong learning keeps your brain healthy
Henry Ford said, "Anyone who stops learning is old, whether at twenty or eighty. Anyone who keeps learning stays young. The greatest thing in life is to keep your mind young." Nearly 100 years later science is validating Henry Ford's quip. Margie E. Lachman, a psychologist at Brandeis University who specializes in aging says, "Education seems to be an elixir that can bring us a healthy body and mind throughout adulthood and even a longer life." Her research has shown that the more education an elderly person has – whether obtained formally or informally — the better they performed on cognitive tests than other elderly folks who had less education.
Learning new things can also help stave off old-age ailments like dementia and Alzheimer's. One study has shown that older folks who stay cognitively active and curious about the world around them are 2.6 times less likely to develop dementia and Alzheimer's than those who let their minds lie fallow.
You'll feel more satisfied with life
In his book Drive, author Dan Pink argues that we need three things to feel motivated about, and satisfied with, our life: autonomy, mastery, and purpose. Becoming a lifelong learner fulfills all three of these psychological needs.
When you're an autodidact you – not your parents, not your professor, not your boss — get to decide what you're going to learn about. Instead of being a passive consumer of knowledge, you're actively choosing what you're learning. In other words, you're autonomous. As you learn new skills, you'll enjoy the positive feeling that comes with mastery. And you'll find yourself with a renewed sense of purpose in life as you set goals for your self-education.
The satisfaction that comes with lifelong learning doesn't stop there. The more you know about the world, the deeper you can plunge into it, and the more levels of it you can experience. Whether you're traveling, conversating, visiting a museum, watching a movie, or reading a book, your library of knowledge helps you make connections that you would never have otherwise perceived. The more you learn, the more you realize how many references and meanings you've missed because the author/speaker simply took that background knowledge, that fluency in cultural literacy, for granted.
You'll become more human. As Robert Heinlein famously put it:
"A human being should be able to change a diaper, plan an invasion, butcher a hog, conn a ship, design a building, write a sonnet, balance >accounts, build a wall, set a bone, comfort the dying, take orders, give orders, cooperate, act alone, solve equations, analyze a new problem, >pitch manure, program a computer, cook a tasty meal, fight efficiently, die gallantly. Specialization is for insects."
Common Perceived Barriers to Becoming a Lifelong Learner
People usually give the same excuses for not taking up the mantle of lifelong learning and instead opting for a life filled with mindlessly surfing the net and watching TV.
Time
I get it. You're busy. I'm sure it's hard to imagine being able to cram in time for self-study when your day is already packed with work and family. But here's the thing: As a lifelong learner, you don't have a deadline on your education. You can take all the time you want and fit it in whenever you'd like. Consequently, you don't need to spend hours a day reading or practicing. Just 30 minutes here and there spread over months and years will do. Moreover, in my experience, when I consciously make learning a priority, I usually end up finding the time for it (meaning I was previously wasting my time doing other stuff).
There are all sorts of spare moments that you can turn into learning opportunities. Listen to an audiobook during your commute instead of the best hits of the 80s, 90s, and today. Bring a good book to read while you're waiting to see your doctor instead of thumbing through a two-year-old copy of Sports Illustrated.
Money
This barrier only exists if you think you need formal classes to learn something. You don't. Thanks to the wonders of the internet you can learn just about anything (and even take college-level classes) at your pace, completely for free. We'll talk about some of these free sources later on in the post.
Information
As with money, this barrier pretty much no longer exists because of the internet. There might be some skills that will require special in-person instruction, but finding those people is also much easier thanks to the web.
Location
This is only a problem if you think you need to be in a formal classroom to learn. You don't. You can learn at home, in your car, or in the garage. Granted, there may be some instances in which you'll need to be in a certain place to be able to learn a new skill (e.g. you can't learn how to snow ski in Oklahoma), but those instances are typically the exception rather than the rule.
How to Become a Lifelong Learner
Foster a growth mindset
One thing that might be keeping you back from learning new things is the belief that you can't learn new things. But neuroscience and psychology have shown this to be false. Our brains remain plastic and malleable well into old age, and it's possible to create new connections among neurons and learn new things even if you're 80 years old.
To become an effective lifelong learner you need to adopt a mindset that is in line with how our brains really work. Stanford psychologist Carol Dweck discovered that people have one of two "mindsets" – fixed or growth. Individuals with a fixed mindset believe that their intelligence and talents are innate and fixed. They don't think they can improve with work and effort. Folks with a growth mindset believe that they can improve themselves through work and practice.
You want to foster a growth mindset. How do you do that? Here are a few things Dweck suggests:
- Reading research that shows growth and improvement is possible
- Developing your resiliency
- Trying new things
- Reading about and extracting lessons from others with a growth mindset
Change your idea of learning
Learning doesn't have to be in a formal classroom setting. In fact, most of the useful stuff you know was probably picked up informally from family, friends, and good old trial and error. To become a lifelong learner, ditch the idea that you need to sign up for a class to actually learn something. Learning opportunities are all around you. Remember that learning isn't confined to what's found in books – acquiring practical skill sets is a big part of it too.
Establish goals
What do you want to learn? When do you want to learn it by? Every year, set goals for yourself on skills and knowledge you want to acquire. I usually set three big learning goals for myself every year. For example, this year my goals are to 1) learn how to create compelling videos for AoM, 2) learn how to handle a handgun in defensive situations, and 3) learn how to hunt and field dress a deer.
Besides those three big goals, I always have the daily goal of learning something new every day whether through reading or by talking to other people. To ensure that we have something else to talk about at dinnertime (besides the blog!), Kate and I play a game called "What did you learn today?" (Actually, we say, "Got any stories for me?" It's our shorthand for, "Have you read or heard anything interesting today?") Every day we both try to learn something new to share with each other over dinner.
It can also be motivating to set a reading goal for yourself. For example, our new employee Jeremy has made it his goal to read all 100 of the books on our "100 Must Read Books for Men" list in 100 months, which comes out to just over eight years. No need to rush things! Jeremy wanted to make sure his goal was manageable, and still be able to do other reading as well. One book per month from the list was the perfect solution.
Find your sources
Once you establish your learning goals, it's time to gather your sources. Do a quick Google search to see what information is available online. After that, head to the library — I always seem to find better and more in-depth insights in books as opposed to web articles. If it's a skill that will require special instruction, start creating a list of places or individuals that could offer that instruction.
Ask questions
Effective learning requires active participation. You can't just passively consume information. While you're reading and talking to experts, ask questions. Don't know what to ask? Check out this great post we published last year on how to ask questions. Don't worry about looking or sounding like an idiot. Swallow your pride.
Find a group
While many of your learning goals can be pursued alone, sometimes it helps to have a group of people to learn along with you. Your fellow learners can provide insights and resources that you never would have thought about. Moreover, in a group setting you'll often get constructive feedback you otherwise wouldn't get alone. As an added bonus, it's just more fun to learn with others.
To find a group of folks to learn with, start with the people you know. Maybe you have some friends that want to learn the same thing as you. Start weekly discussions or practice sessions with them. If you can't find any friends with the same learning goals, check out sites like MeetUp. There's bound to be a group in your area that focuses on your learning goal. While they don't provide the same sort of dynamic interaction as in-person groups, online communities can provide a great social learning environment as well.
Practice, practice, practice
Don't just read or listen your way to knowledge. Try to find a way to put that knowledge to work. If you're learning about art, visit a museum and try to identify which paintings belong to the Romantic period. If you're learning about wilderness survival, get out into the wild every month and put those bushcraft skills to use. If you're learning how to code, code.
Teach what you're learning
Teach what you're learning. One of my all-time favorite books is Stephen Covey's The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People. One of the skills Covey teaches in the book is that to truly learn something you need to teach it. According to Covey, when we teach, we become truly motivated to learn the material because we want to ensure proper instruction. Teaching also forces us to look at a concept with a beginner's mind, which can provide the clarity and insight that we were lacking. Moreover, simply talking aloud to somebody can help you solidify ideas through the "production effect."
As you learn new things, teach it to others. Blogging is a great way to teach what you're learning. Many of the skills I've acquired in the past five years have come from deciding to write a post about a topic. When I wrote "How to Change the Oil in Your Car," I had Kate's Uncle Buzz teach me how; when I wrote "How to Throw a Knife," I went and spent the day with dude ranch owner Tom Warren; and when Kate and I wrote our series on the history of honor, we read dozens of books and scholarly articles on the subject.
Test yourself
It's important to get feedback while you're learning, and testing is the best way to do it. As a self-learner, you're likely not going to face formal tests, so you'll need to create your own. How you test yourself will depend on the skill or knowledge set you're trying to acquire. If you're learning marksmanship, your test could be the U.S. Army's rifle marksmanship scorecard; if you're learning Spanish, your test could be to visit the local Mexican grocery store and talk to the cashier only in Spanish.
Sources for Lifelong Learning
As I mentioned above, there are countless free sources available online. Here are a few of the best(use google):
Coursera
Coursera works with top universities from around the world to offer classes online for free. You can take classes from a variety of disciplines including computer sciences, psychology, and Spanish.
OpenStudy
OpenStudy is a social learning network that allows you to connect with individuals with the same learning goals as you.
Khan Academy
I freaking love Khan Academy. You'll find over 4,000 videos covering topics ranging from algebra to finance to history. My favorite part of Khan Academy, though, is math exercises. You start with basic math and work your way up to calculus in an adaptive, game-like environment. I've been slowly going through the exercises to freshen up on my math.
Duolingo
Free website to learn foreign languages. It's a pretty cool set up. As you progress through the lessons, you're simultaneously helping translate websites and other documents.
Code Academy
Learn to code for free with interactive exercises. I wish Code Academy was around when I was learning how to build AoM. It would have helped a lot.
edX
Harvard University and MIT partnered together to create interactive, free online courses. The same world-renowned professors that teach at Harvard and MIT have created the courses on edX. You can find courses for just about any subject. I've signed up for a class called The Ancient Greek Hero. Class started last week, but you can still sign up. Join me!
Udacity
Udacity is similar to edX and Coursera. College level classes taught online for free.
CreativeLive
I discovered CreativeLive a few weeks ago. It's an interesting concept. You can watch the live stream of the course being taught for free, but if you want to view the course later and at your own pace you have to pay for it. The courses focus on more creative and business subjects like videography and online marketing. I've sat in on a few of the free courses and was impressed with the curriculum.
TED
TED compiles speeches and lectures not only by professors but interesting people from many different walks of life. TED talks are lighter than academic lectures, often quite funny, and concentrate on interesting ideas and concepts. And most are 20 minutes or less, so they're great for those with a short attention span.
iTunes U
Download thousands of free podcast lectures taught by the best professors from around the world and learn while in your car.
YouTube EDU
Instead of watching a bunch of auto-tuned cats, enrich your mind by browsing through YouTube EDU. They have thousands of videos that cover a variety of topics.
Limiters in PFSENSE
The limiter feature allows you to setup Dummynet pipes. Dummynet was designed to be able to simulate any kind of network connection. You can simulate a dialup connection, a T1, a T1 run through a microwave oven, or a satellite connection to the Moon. A side effect of being able to simulate any type of network connection is that you can use them to limit the amount of bandwidth a host or group of hosts have access to. Both the packet shaper and limiters can be used at the same time so you can shape your traffic as a whole, and also limit certain traffic to a certain amount of bandwidth. There are 2 basic steps to setting up a limiter to control bandwidth. Setup the limiters you will be using. Assign traffic to those limiters.
Setup Limiters
Limiters are setup by creating them under Firewall > Traffic Shaper, on the Limiters tab. You can use just one pipe for both inbound and outbound traffic, but that would mean you are simulating a half-duplex connection. The recommended method is to create 2 pipes, one for inbound traffic and one for outbound traffic. The direction is from the perspective of the interface. If using limiters on LAN, the inbound queue is your upload and the outbound queue is your download. You should name the pipes so that you will easily remember which one is which, such as InLimitLan and OutLimitLan.
Dynamic queue creation
Dummynet pipes have a feature called dynamic queue creation which allows you to have a unique queue based on the uniqueness of a connections source protocol, ip, source port, destination ip or destination port. They can also be used in combination. pfSense currently only allows setting the source address or the destination address as the mask, meaning that you can give each host behind your firewall its own set of pipes so that each node is restricted to using a certain amount of bandwidth. To do this you would give your In pipe a Source Address mask, so that each host sending packets gets it's own dynamic pipe for uploading. You would give your Out pipe a destination address mask, so that each host receiving packets gets it's own dynamic pipe for downloading.
Assign Traffic
Once you setup a limiter pipe, the next step is to assign traffic to it by setting the "in/out" option in a firewall rule. Remember that in and out are from the perspective of that interface on the firewall. If you're choosing limiters on the LAN interface, "out" is download speed (traffic from the LAN NIC into the LAN) and "in" is upload speed (traffic from the LAN into the LAN NIC). Simply creating the limiters does not do anything, you must assign them on a firewall rule for them to be used.
Limiter status
The bandwidth usage and other limiter information is available under Diagnostics>Limiter Info.
Captive Portal Notes
Captive portal can automatically setup its own pipes for each logged in user, no need to set this up manually. Take a look at the captive portal setup page to set this up.
Using Limiters for Bandwidth Guarantees
If you want to use limiters to guarantee a certain amount of bandwidth instead of limit, you can do so by making four limiters:
- Bandwidth to guarantee upload
- Bandwidth to guarantee download
- Total bandwidth upload (less guaranteed above)
- Total bandwidth download (less guaranteed above)
Ensure that you do not set the Mask to anything other than "none". It must be "none" for these to work properly. So if you have 8Mb down and 2Mb up, and you want to guarantee 512Kb/s for service X, you'd have queues sized like so:
- 512 Kb/s
- 512 Kb/s
- 1536 Kb/s
- 7680 Kb/s
Then direct the guaranteed service traffic into the first two limiters, and everything else into the "total" limiters.
UnOfficial Directions:
Go to the Firewall>>>Traffic Shaper option
Create a new limiter, make sure Enable is checked, name it "500dest", set bandwidth to 500Kbit/s, set mask to destination. Save it.
Create another limiter, make sure Enable is checked, name it "500src", set bandwidth to 500Kbit/s, set mask to source. Save it.
Make sure to apply changes.
Create an alias with all the ip's you want in Firewall>>> Aliases
Name it, save it.
Apply changes.
Go to firewall>>>Rules>>>LAN
Create a new rule. Protocol type ANY, Set the alias(or ipaddress) as the source, scroll down click advanced next to in/out, set the first to 500src, the second to 500dest. Make sure your new rule is higher than any default allow out.
Apply changes and test it out.
Alternatively you could edit the LAN default allow out and add the In/Out option there and it would apply to every host on the LAN individually (each host individually limited to 500Kbps/500Kbps).
Setup information for Linux and Virtual Box:
Mounting NTFS Share Command:
mount.vboxsf -w -o fmode=0777,dmode=0777 folder_name /mnt/path_to_mount_point- Where fmode and dmode set permissions, folder_name is what you named the folder within the VirtualBox settings and the /mnt/path folder must already exist.
Cloning a Virtual Machine via command line:
C:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage.exe clonevdi "\path_to_vdi_to_be_cloned" "\path_to_where_cloned_vdi_should_go"
woot.
Deadlift is one of the best workouts that you can do for your lower back, trapezius, upper back, abdominals, hamstrings, hips, gluteus maximus, quadriceps, annnnnnddd forearms. Here is how to do them properly:
- Start off with light weight, you want to make sure you have proper form before you begin lifting heavier weight.
- Set your stance: Approach the bar so that the center of both your feet are directly under the bar with your stance slightly less than should width apart to make sure there's room for you arms. Make sure your toes are either pointing forward or slightly outward.
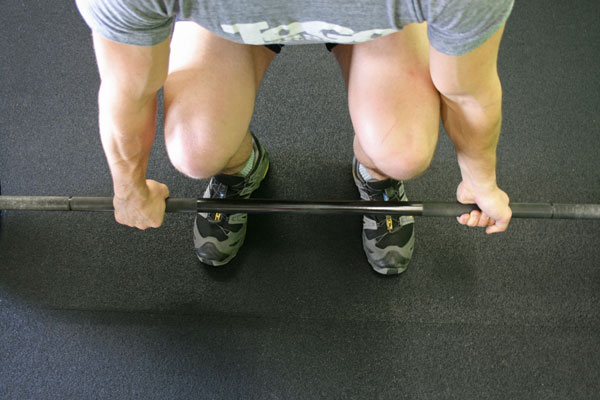
- Squat: Bend your knees while keeping your back straight, so that you are sitting over your knees with your head up.

- Grab the Bar: Grab the bar with a grip slightly wider than shoulder width outside of your legs. It is recommended that you use the alternating grip, or, one palm facing you and the other facing away. This method will stabilize the bar and keep it from slipping out of your hands.
- Set your hips and legs: Lower your hips so that your thighs are parallel to the floor. Keep the lower parts of your legs mostly vertical. The angle between your foot and lower leg should b eclose to 90 degrees. Keep in mind, in the squat image above your back should be straighter.
- Lift the bar: Stand up by raising your hips and shoulders at the same rate and maintain a flat back. Keep your abdominals tight during the whole lift. Do your best to lift the bar straight up vertically along your shins and close to your body thinking of it as pushing the floor away. Come to a complete standing position with shoulders back. Let the bar hang in front of your hips.
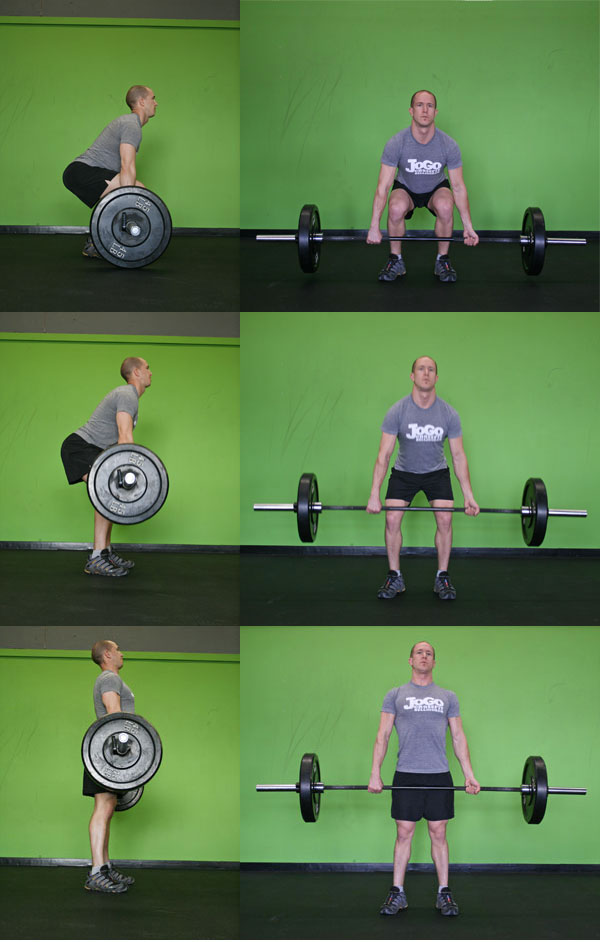

- Lower the Bar: Keep your back straight and stick your gluteus maximus out as needed as if you were sitting down in to a chair while keeping your head up.
Tips: * Looking forward helps keep balance and alightment of the spine. * Imagine that you're tryign to touch the wall behind you with your butt and the wall in front of you with your chin.
Head Tilt
How you hold your head is key to overall posture, which determines how efficiently you run. Let your gaze guide you. Look ahead naturally, not down at your feet, and scan the horizon. This will straighten your neck and back, and bring them into alignment. Don't allow your chin to jut out.
Shoulders
Shoulders play an important role in keeping your upper body relaxed while you run, which is critical to maintaining efficient running posture. For optimum performance, your shoulders should be low and loose, not high and tight. As you tire on a run, don't let them creep up toward your ears. If they do, shake them out to release the tension. Your shoulders also need to remain level and shouldn't dip from side to side with each stride.
Arms
Even though running is primarily a lower-body activity, your arms aren't just along for the ride. Your hands control the tension in your upper body, while your arm swing works in conjunction with your leg stride to drive you forward. Keep your hands in an unclenched fist, with your fingers lightly touching your palms. Imagine yourself trying to carry a potato chip in each hand without crushing it. Your arms should swing mostly forward and back, not across your body,between waist and lower-chest level. Your elbows should be bent at about a 90-degree angle. When you feel your fists clenching or your forearms tensing, drop your arms to your sides and shake them out for a few seconds to release the tension.
Torso
The position of your torso while running is affected by the position of your head and shoulders. With your head up and looking ahead and your shoulders low and loose, your torso and back naturally straighten to allow you to run in an efficient, upright position that promotes optimal lung capacity and stride length. Many track coaches describe this ideal torso position as "running tall" and it means you need to stretch yourself up to your full height with your back comfortably straight. If you start to slouch during a run take a deep breath and feel yourself naturally straighten. As you exhale simply maintain that upright position.
Hips
Your hips are your center of gravity, so they're key to good running posture. The proper position of your torso while running helps to ensure your hips will also be in the ideal position. With your torso and back comfortably upright and straight, your hips naturally fall into proper alignment--pointing you straight ahead. If you allow your torso to hunch over or lean too far forward during a run, your pelvis will tilt forward as well, which can put pressure on your lower back and throw the rest of your lower body out of alignment. When trying to gauge the position of your hips, think of your pelvis as a bowl filled with marbles, then try not to spill the marbles by tilting the bowl.
Legs/Stride
While sprinters need to lift their knees high to achieve maximum leg power, distance runners don't need such an exaggerated knee lift--it's simply too hard to sustain for any length of time. Instead, efficient endurance running requires just a slight knee lift, a quick leg turnover, and a short stride. Together, these will facilitate fluid forward movement instead of diverting (and wasting) energy. When running with the proper stride length, your feet should land directly underneath your body. As your foot strikes the ground, your knee should be slightly flexed so that it can bend naturally on impact. If your lower leg (below the knee) extends out in front of your body, your stride is too long.
Ankles/Feet
To run well, you need to push off the ground with maximum force. With each step, your foot should hit the ground lightly--landing between your heel and midfoot--then quickly roll forward. Keep your ankle flexed as your foot rolls forward to create more force for push-off. As you roll onto your toes, try to spring off the ground. You should feel your calf muscles propelling you forward on each step. Your feet should not slap loudly as they hit the ground. Good running is springy and quiet.
Here's a quick post about some useful Windows commands, these can get you out of trouble if you don't have admin rights on a user account and other tricky situations...:
Runas elevated command prompt:
General Usage:
Runas /user:%domain%\%username% %command%Example:
Runas /user:mydomain\myaccount cmd
- Uninstall an application:
- appwiz.cpl (This opens add/remove programs)
Manage local users and groups on a remote machine:
General Usage:
Lusrmgr.msc -a /computer=%computername%Example:
Lusrmgr.msc -a /computer=deepthoughtFull Descriptions: Your domain account does not have admin rights on the remote machine? Synchronize your local admin password with the local admin password on the remote machine. Then open a runas window on your system as the local admin and run the local users and groups console (lusrmgr.msc) targeted to the remote machine and give your domain account access.
Activate Hidden Administrator Account:
Enable:
net user administrator /active:yesDisable:
net user administrator /active:no
Dism Commands in Windows 8:
- In Windows 8 Imagex has been depracated and the command to use nowadays is DISM. Dism can do all of the same things that imagex could do such as append images to one another expanding the index size for 1 to many. Also, It can apply images and add drivers to and freshly installed Windows Installation.
This command goes through a folder adding all .inf files that apply:
dism.exe /image:C:\ /Add-Driver /Driver:C:\drive_location /Recurse /ForceUnsignedApply an image:
dism.exe /apply-image /imagefile:D:\monkey.wim /index:1 /ApplyDir:C:\Capture an image:
Dism /Capture-Image /Compress:maximum /ImageFile:{PATH TO WIM} /CaptureDir:{DRIVE TO CAPTURE} /Name:"My Windows partition"
Native booting VHDS
Create VHD with Diskpart For production environments the Microsoft recommends using fixed VHD type:
create vdisk file=C:\VHDs\{name}.vhd maximum={MAXMB} type=expandable select vdisk file=C:\VHDs\{name}.vhd attach vdisk create partition primary format fs=ntfs quick assign letter={VHDLetter}Setting VHD as a Native Boot option (Source: VHD)
cd {VHDLetter}:\windows\system32 bcdboot {VHDLetter}:\windows